Molluscum contagiosum: Signs and symptoms
Molluscum contagiosum is generally a harmless skin infection. You’ll often see small, firm bumps on the skin.
These bumps can appear anywhere on the skin; however, children usually get them on their:
Torso
Armpits
Knees (especially the backs of)
Arms (especially in the crooks)
Groin area
Mollusca (the bumps) rarely appear on the palms or the soles, but you can get them in the moist tissue that lines the inside of your eyelids.
What does molluscum contagiosum look like?
The following pictures show you what molluscum contagiosum tends to look like. This lineup begins by showing you what the bumps look like when they first appear and ends with what you may see right before the skin clears.
First sign
The bumps appear on the skin between 2 and 8 weeks after you get the virus that causes this skin infection.
When the bumps first appear, you usually see ones that are small, firm, pink, flesh-colored, or white. These bumps will likely get bigger.

Dome-shaped bumps
As the bumps grow, they become dome-shaped and develop an indent in the center, which can look like someone pushed a pin into the middle.

Molluscum on eyelid
When a bump develops on an eyelid, it often looks like a water blister, as shown here.
Having molluscum on an eyelid can cause frequent pink eye. When the molluscum contagiosum clears, the pink eye also tends to disappear.

Spreading bumps
Scratching or picking at one or more bumps and then touching skin without the molluscum contagiosum can spread the virus to other areas of your skin.
In time, new bumps appear. Some people have widespread bumps, as shown here.

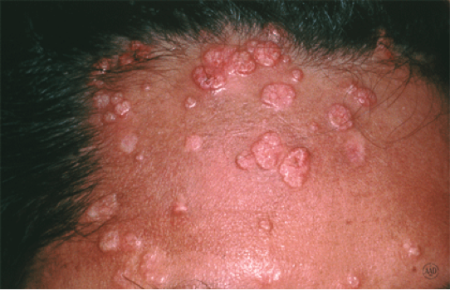
Large bumps
Having a weakened immune system, due to an organ transplant, cancer treatment, or an HIV infection, can cause large bumps.
Clusters of large bumps, such as shown here on this man’s forehead, can appear.
Bumps about to clear
When the bumps become red and look like pimples, it means your body is fighting off the virus.
This change is a good sign. It means the bumps will soon clear.

Does molluscum contagiosum cause pain?
This skin infection is usually only painful when scratching or rubbing infects the bumps with bacteria.
Sometimes, the bumps feel itchy.
How long does it take for the bumps to go away?
The body can clear the bumps on its own, but this can take time. You may see new bumps for several months. As some bumps clear, new ones can appear. This cycle usually lasts about 6 to 18 months before the skin clears completely.
Sometimes, clearing takes longer. New bumps can continue to appear for 3 or 4 years, and there have been reports of molluscum contagiosum lasting 5 years.
There’s no way to know how long it will take for your bumps to clear.
Treatment can help clear the bumps more quickly. You can find out who is likely to need treatment at: Molluscum contagiosum: Causes.
Images
1: Getty Images
2, 5: Image used with permission of the American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
3, 4, 6: Images used with permission of DermNet NZ.
References
Dohil MA, Lin P, et al. “The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children.” J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(1):47-54.
van der Wouden JC, van der Sande R, et al. “Cochrane Review: Interventions for cutaneous molluscum contagiosum.” Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;5:CD004767.
Wanat KA, AR, et al. “Bedside diagnostics in dermatology: Viral, bacterial, and fungal infections.” J Am Acad Dermatol 2017;77:197-218.
 Atopic dermatitis: More FDA-approved treatments
Atopic dermatitis: More FDA-approved treatments
 Biosimilars: 14 FAQs
Biosimilars: 14 FAQs
 How to trim your nails
How to trim your nails
 Relieve uncontrollably itchy skin
Relieve uncontrollably itchy skin
 Fade dark spots
Fade dark spots
 Untreatable razor bumps or acne?
Untreatable razor bumps or acne?
 Tattoo removal
Tattoo removal
 Scar treatment
Scar treatment
 Free materials to help raise skin cancer awareness
Free materials to help raise skin cancer awareness
 Dermatologist-approved lesson plans, activities you can use
Dermatologist-approved lesson plans, activities you can use
 Find a Dermatologist
Find a Dermatologist
 What is a dermatologist?
What is a dermatologist?